Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Geographic and Temporal Patterns#
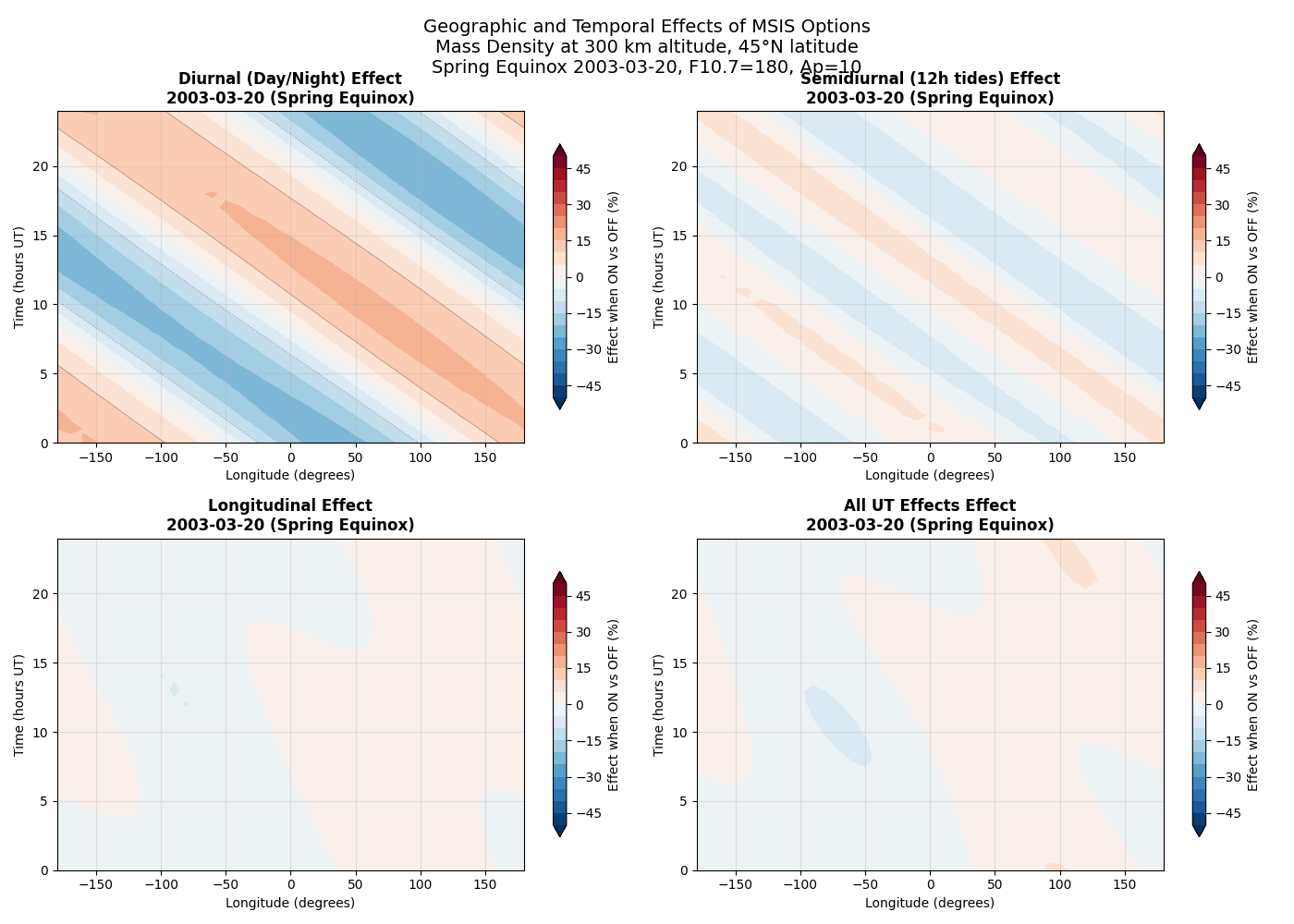
This example demonstrates how different MSIS options affect atmospheric density across longitude and time. The plots show surface maps of mass density at 300 km altitude, revealing the geographic and temporal patterns controlled by each option.
Four key MSIS options with strong spatial/temporal patterns are highlighted: 1. Diurnal variations (day/night differences) 2. Semidiurnal tidal effects (12-hour cycles) 3. Longitudinal variations (geographic differences) 4. Universal Time effects (UT dependencies)
This complements the altitude overview by showing horizontal structure patterns.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pymsis
# Define grid parameters
lons = np.linspace(-180, 180, 37) # 10-degree longitude spacing
times = np.linspace(0, 24, 25) # Hourly through one day
lat = 45 # Mid-latitude
alt = 300 # Thermosphere where effects are clear
f107 = 180
f107a = 160
ap = 10
# Create date array for one day
base_date = np.datetime64("2003-03-20") # Spring equinox - sun centered on equator
dates = [base_date + np.timedelta64(int(h), "h") for h in times]
# Select key options that show strong geographic/temporal patterns
key_options = {
"Diurnal (Day/Night)": 6, # Index 6 = diurnal
"Semidiurnal (12h tides)": 7, # Index 7 = semidiurnal
"Longitudinal": 10, # Index 10 = longitudinal
"All UT Effects": 9, # Index 9 = all UT effects
}
# Create figure with subplots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(14, 10))
axes = axes.flatten()
# Create aps array for single calculations
aps_single = [[ap] * 7] # Array of arrays for single date calculations
for plot_idx, (option_name, option_idx) in enumerate(key_options.items()):
ax = axes[plot_idx]
# Create meshgrid for plotting
LON, TIME = np.meshgrid(lons, times)
density_on = np.zeros_like(LON)
density_off = np.zeros_like(LON)
# Calculate density for each lon/time combination
for i, _ in enumerate(times):
date = dates[i]
# All options ON
options_on = [1] * 25
result_on = pymsis.calculate(
date, lons, lat, alt, f107, f107a, aps_single, options=options_on
)
density_on[i, :] = np.squeeze(result_on)[:, pymsis.Variable.MASS_DENSITY]
# Target option OFF
options_off = [1] * 25
options_off[option_idx] = 0
result_off = pymsis.calculate(
date, lons, lat, alt, f107, f107a, aps_single, options=options_off
)
density_off[i, :] = np.squeeze(result_off)[:, pymsis.Variable.MASS_DENSITY]
# Calculate relative difference (%)
relative_diff = 100 * (density_on - density_off) / density_on
# Create contour plot
levels = np.linspace(-50, 50, 21)
contour = ax.contourf(
LON, TIME, relative_diff, levels=levels, cmap="RdBu_r", extend="both"
)
# Add contour lines for clarity
ax.contour(
LON,
TIME,
relative_diff,
levels=levels[::4],
colors="black",
alpha=0.3,
linewidths=0.5,
)
ax.set_title(
f"{option_name} Effect\n{base_date} (Spring Equinox)",
fontsize=12,
fontweight="bold",
)
ax.set_xlabel("Longitude (degrees)")
ax.set_ylabel("Time (hours UT)")
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Add colorbar
cbar = plt.colorbar(contour, ax=ax, shrink=0.8)
cbar.set_label("Effect when ON vs OFF (%)", fontsize=10)
# Add overall title
fig.suptitle(
f"Geographic and Temporal Effects of MSIS Options\n"
f"Mass Density at {alt} km altitude, {lat}°N latitude\n"
f"Spring Equinox 2003-03-20, F10.7={f107}, Ap={ap}",
fontsize=14,
y=0.98,
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.88)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.737 seconds)
